On Sep. 7, the National Health Committee (NHC) revealed the drafts for infant formula and follow-up formula standards.
NHC made certain important revisions to the existing standards, for instance the older infant and young children formula standard was split to two standards. Coordinated with Chinese universities, the levels of nutrients were widely revised based on the breast milk studies, NHC said in the revision instruction. Antion will introduce the key changes and elaborate influences on formulation registration in this article.
Key changes
Draft of infant formula standard (draft GB 10765, for 0-6 months)
Choline is required as an essential nutrient and the required level is doubled while it is an optional nutrient in the existing standard
For carbohydrate source, in current standard, lactose, lactose and glucose polymer are preferred, and fructose is forbidden in case of potential life-threatening symptoms in young infants with unrecognized hereditary fructose intolerance. In the draft, Lactose is the preferred carbohydrate source and glucose polymer in proper level is acceptable while both sucrose and fructose are forbidden
The max and min level for nutrients are changed, especially vitamin D, please check the annex
Each strain of probiotics should reach a potency of 10^6 cfu/g (ml)
A small change* on mandatory warning may lead to label revision
* “對于0-6月的嬰兒最理想的食品是母乳,在母乳不足或無母乳時可食用本産品” is changed to “對于0-6月齡的......”
Draft of older infant formula standard (draft GB 10766, for 7-12 months)
Choline, manganese, selenium are required as essential nutrients while they are optional in the existing standard
Whey protein of milk-based product should be no less than 40% of total protein content
Ingredients and food additives should not contain gluten
In the draft, lactose is the preferred carbohydrate source and should be no less than 90%, glucose polymer in proper level is acceptable while both sucrose and fructose are forbidden
The max and min level for nutrients are changed, especially vitamin D, please check the annex
Each strain of probiotics should reach a potency of 10^6 cfu/g (ml)
A small change* on mandatory warning may lead to label revision
*suitable for 6-12 months is changed to 7-12 months
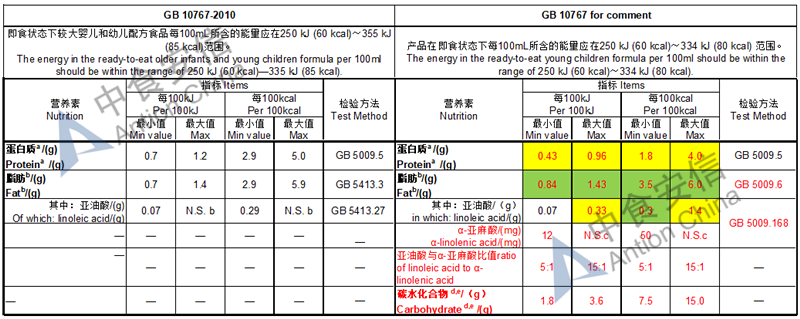
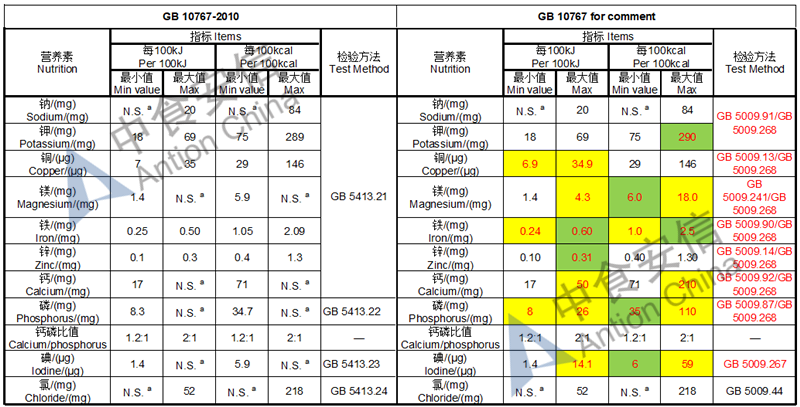
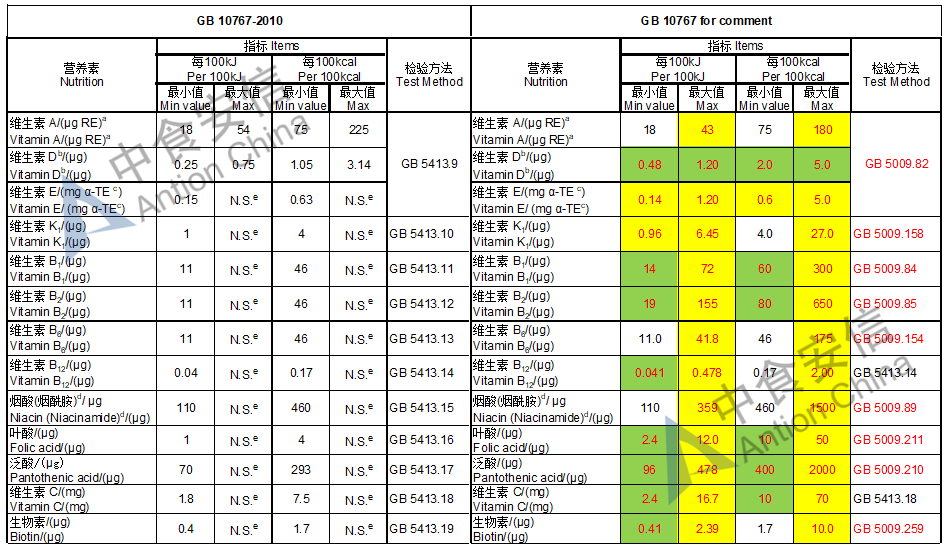
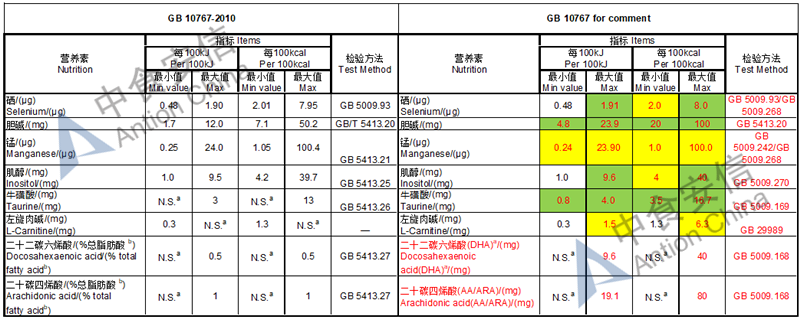
Draft of young children formula standard (draft GB 10767, for 13-36 months)
Lower protein level
In the draft, except the lactose-free or low lactose formula, lactose should be no less than 50% of total carbohydrate
The max and min level for nutrients are changed, especially vitamin D, please check the annex
Each strain of probiotics should reach a potency of 10^6 cfu/g (ml)
A small change* on mandatory warning may lead to label revision
*suitable for 12-36 months is changed to 13-36 months
Influences on formulation registration
The new drafts are still in consultation period. It may take 4 years for these standards to go through the publishment and transitional period, and finally get fully implemented. So for registered formulas, the influence is very limited. We just suggest the R&D to initiate the formula update. As for products haven’t obtain the registration, it would be better to get the registration quickly to avoid the situation that the standards are published before the completion of registration.
According to the draft of the guideline for changing application of formulation registration, we consider that any additions of new nutrients or NIP changes may be recognized as a new formula and need to apply for a new registration certificate.
Annex
Comparison of infant formula standard (draft GB 10765, for 0-6 months)
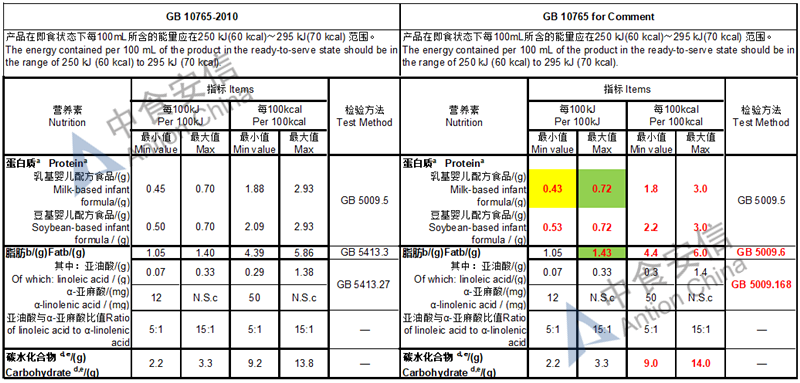
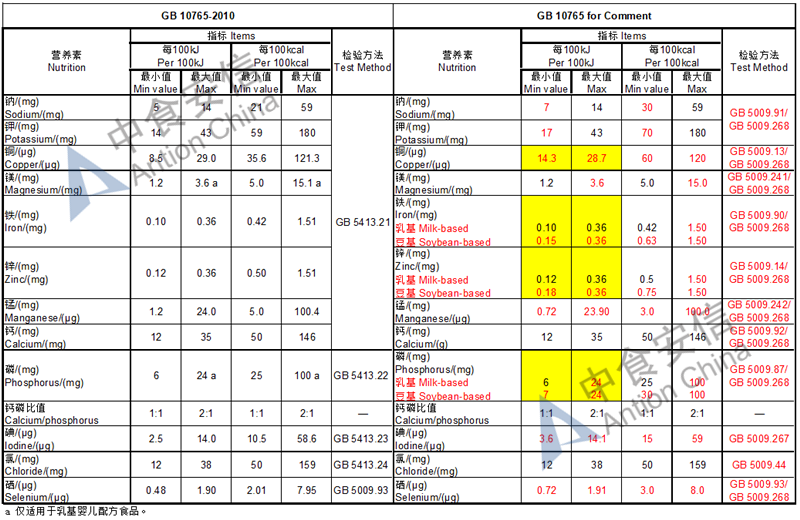
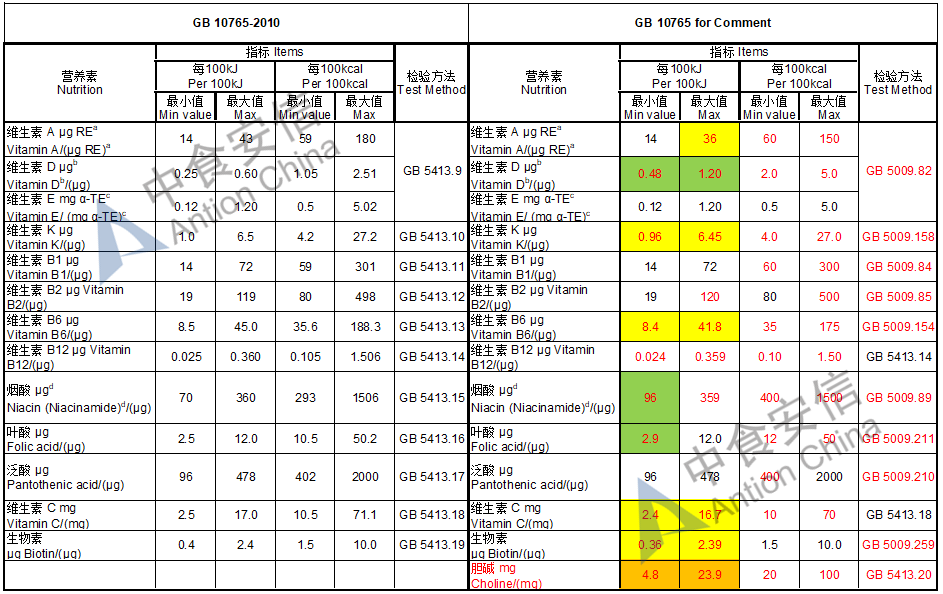
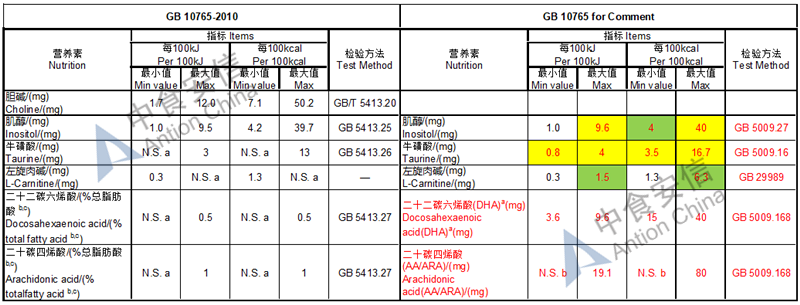
Comparison of older infant formula standard (draft GB 10766, for 7-12 months)
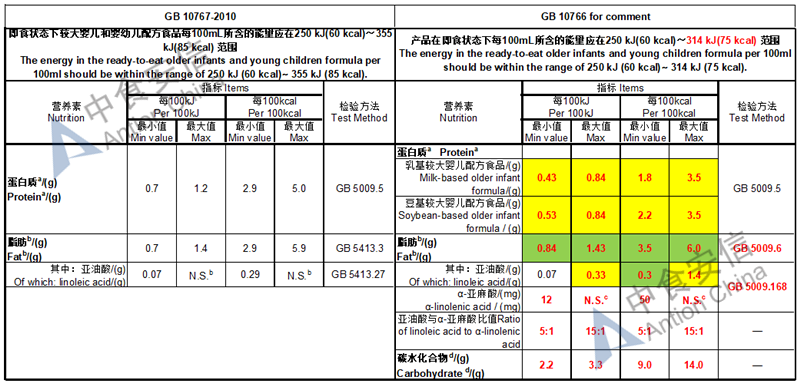
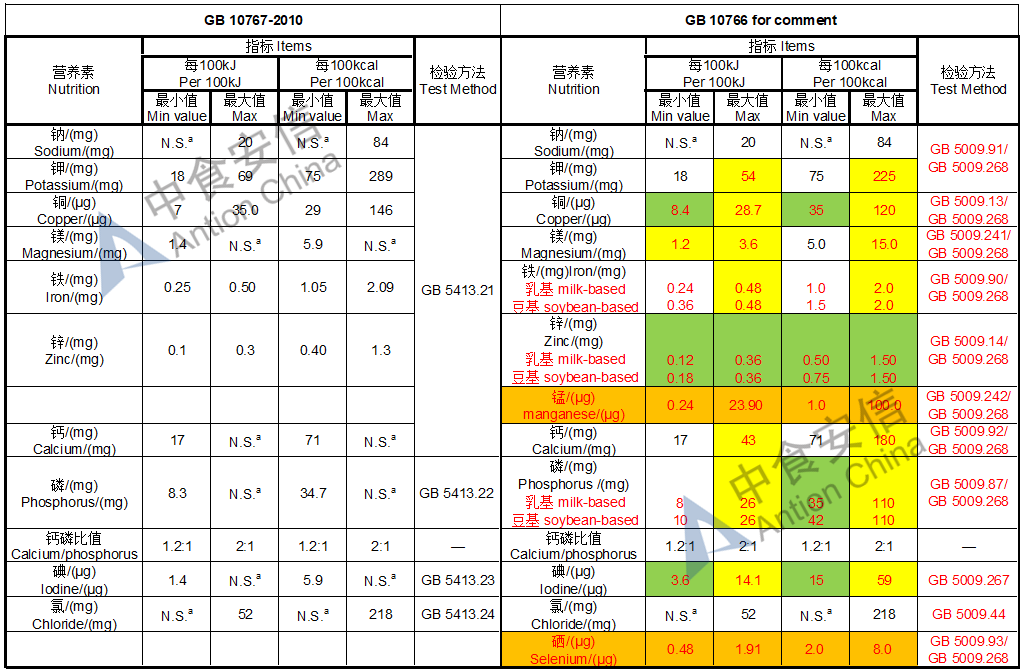
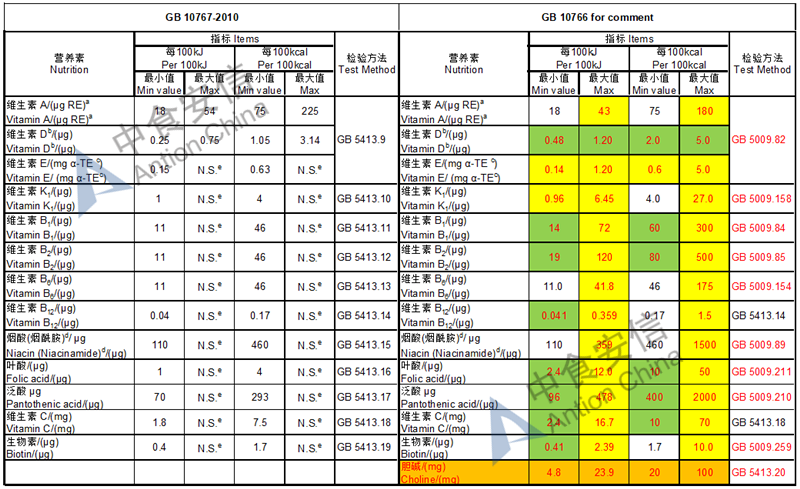
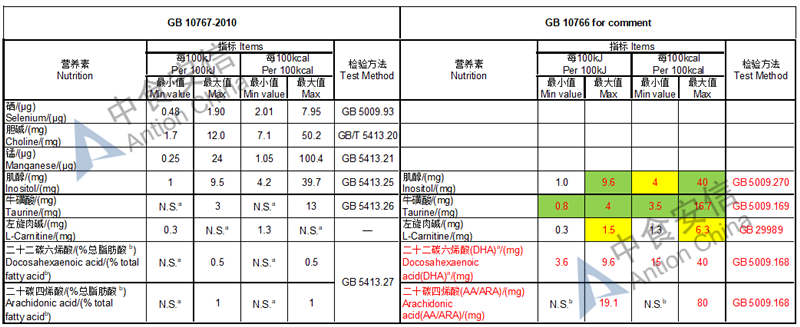
Comparison of young children formula standard (draft GB 10767, for 13-36 months)
Relevant Reading
Introduction of Food Related Application & Registration Services